Detecting and Reducing Hallucinations in Factual Question Answering
Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in factual question answering in recent years, but they sometimes give the answer with hallucinations — responses that seem to be the correct answer but in fact incorrect. Hallucinations give significant challenges for deploying LLMs in reliable medical knowledge queries, which require a high degree of confidence in the resulting output. This study followed the ideas from the paper “On Early Detection of Hallucinations in Factual Question Answering”.
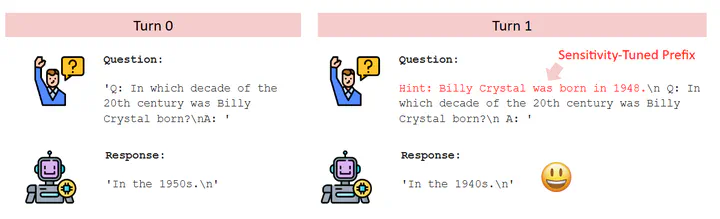
A multi-turn recursive framework for detecting and mitigating hallucinations in large language models (LLM) responses to factual questions was implemented using the Open-llama-7B model. The pipeline leverages a trained classification models guide a language model in its recursive generation. To reduce semantic entropy in the resulting output, a sensitivity hint prefix prompting method was adopted to reduce the hallucination rate in the TriviaQA dataset.
Overall, a recursive generation pipeline with a known prior of whether an answer is hallucinating or not shows promising results. The next phase of the project involves adapting the same architecture for medical Q&A datasets for improved generative response of medical LLMs.