REPO LINK HERE Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in factual question answering in recent years, but they sometimes give the answer with hallucinations — responses that seem to be the correct answer but in fact incorrect. Hallucinations give significant challenges for deploying LLMs in reliable medical knowledge queries, which require a high degree of confidence in the resulting output. This study followed the ideas from the paper “On Early Detection of Hallucinations in Factual Question Answering”. A multi-turn recursive framework for detecting and mitigating hallucinations in large language models (LLM) responses to factual questions was implemented using the Open-llama-7B model. The pipeline leverages a trained classification models guide a language model in its recursive generation. To reduce semantic entropy in the resulting output, a sensitivity hint prefix prompting method was adopted to reduce the hallucination rate in the TriviaQA dataset. Overall, a recursive generation pipeline with a known prior of whether an answer is hallucinating or not shows promising results. The next phase of the project involves adapting the same architecture for medical Q&A datasets for improved generative response of medical LLMs.
May 1, 2025
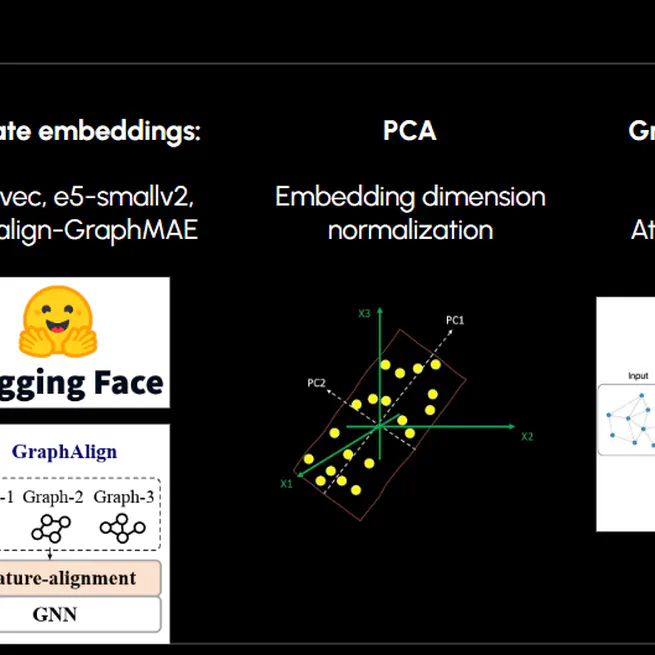
REPO LINK HERE Scaling and generalizing cross-domain tasks amongst graph datasets remains a challenge due to the variability in node features, edge-based relationships, and the inherit challenges for transfer-learning amongst graphs. The aim of this project is to explore the capabilities of using language embeddings to achieve task generalizations across different graph structures and build models that could learn cross-domain relationships. By evaluating the performance of trained graph neural networks across different language embeddings, the authors evaluate the effectiveness of various encoding architectures. Contrary to expectations, the simpler word2vec achieved greater performance compared to the E5-Small-V2 and GraphAlign pre-trained embeddings. Finally, the author discusses limitations and the conclusiveness of the study and discusses future research directions in unifying cross-domain graphs with scalable architecture.
May 1, 2025
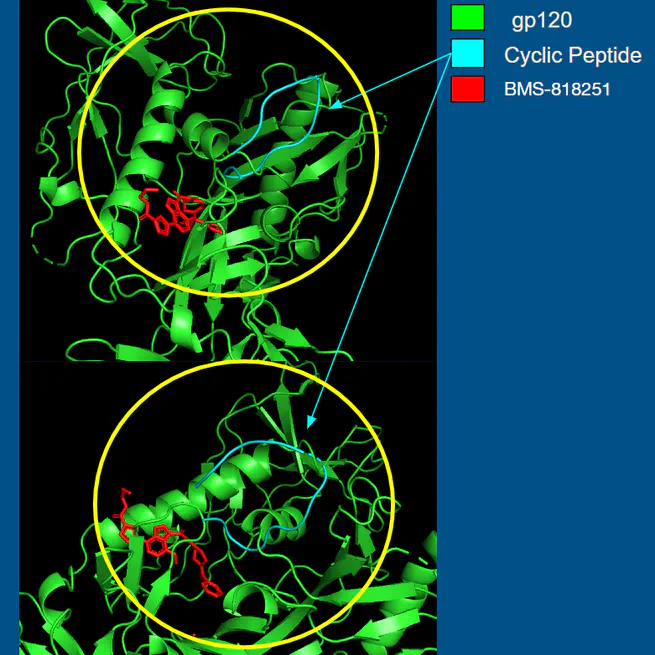
PAPER This independent research study conducted a series of investigations to enhance the precision of cyclic peptide generation targeting the HIV gp120 trimer. The methods included proximity mapping to focus on the CD4 binding site, centroid distance penalization, generative loss tuning, and the development of custom generative functions. By synthesizing these findings, a novel methodology was implemented to generate candidate cyclic peptides of varying lengths. This process successfully produced cyclic peptides that resemble the crystal structure of CD4 attachment inhibitor (BMS-818251 molecule). This new methodology demonstrated improved control and precision in the generation of compounds, thereby enhancing the applicability of AlphaFold in the drug discovery process.
Jan 30, 2025

This is an ongoing research project into methods to improve tracking of environmental contamination and infection tracking through the use of Digital Twins in hospitals.
Apr 15, 2024
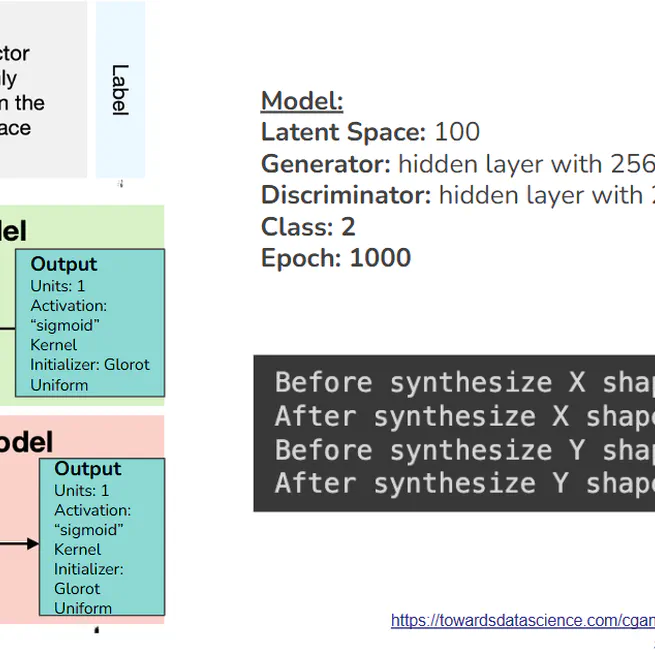
REPO LINK HERE Strokes represent a major global health concern, being one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. As medical science advances, the ability to predict and prevent stroke occurrences through early detection has become increasingly crucial. Strokes resulting from an abrupt interruption of blood flow to the brain, can lead to permanent brain damage or death. With the incidence of stroke doubling in the last three decades, and an estimated one stroke occurring every three seconds around the globe, it is clear that this is a condition that affects individuals across all age groups, not just the elderly. Recognizing the key indicators of high stroke risk in patient health records can significantly aid in mitigating this trend. Through interventions such as lifestyle modifications and targeted medical treatments, healthcare providers can dedicate resources more effectively to reduce the occurrence of strokes and manage their aftermath, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden on health systems. The focus of this project is to meticulously analyze various algorithms to identify the most effective approach for predicting stroke occurrences. In the quest to address this pressing medical challenge, the report will explore different machine learning models, utilizing patient health records from Kaggle [1] as a dataset. The objective is to pinpoint an algorithm that excels in accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, thereby enabling healthcare providers to intervene proactively and allocate medical resources efficiently to at-risk individuals. By leveraging data-driven insights, it is hoped that the algorithm can contribute to the global efforts in reducing stroke incidences and the associated healthcare burdens. Methods explored: EDA Oversampling techniques with (SMOTE, ADSYN) Data Augmentation with cGAN ML prediction (Logistics regression, random forest, gradient boosting, SVM) Deep learning (hyperparmeter tuning with neural networks)
Nov 20, 2023

(REPO LINK HERE)[https://github.com/jethrocsau/msbd5003-random-forest] Abstract: In this study, we will leverage the Spark Python API to execute the random forest algorithm. This distributed variant of the random forest tree has the capacity to manage large datasets, and offers parallel training to increase the overall training time. To appraise the performance and scalability of the distributed random forest, we have conducted a comparative analysis on various factors. These include the algorithm’s performance across different dataset sizes, executor counts, numbers of RDD partitions, and its performance in comparison to the built-in available algorithm in MLlib.
Apr 30, 2023

REPO LINK HERE As an exploratory project, finetuned the YOLOv5 model for enhanced multi-orientation face mask detection for enhanced PPE training in job site. Yolov5 finetuning with backbone layers frozen using data-augmented images of face masks in multiple angles and orientations.
Sep 1, 2022